The Ultimate Guide To Lumens and Lighting
What are lumens and why are they important?
Lumens are a unit of measurement used to quantify the amount of visible light emitted by a light source. More specifically, lumens measure the total amount of light output by a light source in all directions, regardless of where the light is being directed or focused.
Lumens are important because they allow us to compare the brightness of different light sources. For example, a light bulb that produces 800 lumens will be brighter than one that produces 500 lumens. This makes it easier to choose the right light source for different applications, whether it's for indoor lighting, outdoor lighting, or specialized applications such as photography or film.
In addition, lumens are also used to calculate the efficiency of lighting systems. The more lumens produced per watt of energy consumed, the more efficient the lighting system is. This is important because it can help to reduce energy consumption and operating costs, as well as minimize environmental impact.
What is the relationship between lumens and brightness?
Lumens and brightness are directly related, as lumens are used to measure the perceived brightness of a light source. The more lumens a light source emits, the brighter it will appear to the human eye.
To understand this relationship better, it's important to know that our perception of brightness is not based solely on the amount of light emitted by a source. Other factors such as the color temperature of the light and the reflectivity of surfaces in the space can also affect our perception of brightness.
However, lumens provide a useful standard for comparing the brightness of different light sources under standardized conditions. For example, a 100-watt incandescent bulb typically emits around 1600 lumens, while a 60-watt incandescent bulb emits around 800 lumens. This means that a 100-watt bulb will appear brighter than a 60-watt bulb when used in the same space.
How is a lumen defined?
In very technical terms, a lumen is defined as the amount of light that is radiated by a light source within a solid angle of one steradian, which is equal to the amount of light emitted by a uniform point source with a luminous intensity of one candela within a cone with a solid angle of one steradian.
In simpler terms, lumens measure how bright a light source is. The higher the number of lumens, the brighter the light source will appear to the human eye. This makes lumens an important factor to consider when selecting light bulbs or fixtures for a given space or application, as they can help ensure that the lighting is appropriate for the intended use and provides sufficient illumination.
How are lumens different from watts?
Lumens and watts are different in that lumens measure the amount of visible light emitted by a light source, while watts measure the amount of power consumed by the light source. In other words, lumens indicate the brightness of a light source, while watts indicate its energy consumption.
In the past, people used to rely on watts as a way of determining a bulb's brightness. However, as energy-efficient bulbs have become more prevalent, watts are no longer a reliable indicator of brightness. For example, a traditional incandescent light bulb might consume 60 watts of power and emit 800 lumens of light, while a modern LED bulb might consume only 9 watts of power and emit the same 800 lumens of light.
Because of this, lumens are now the standard measure of a bulb's brightness, and are used to help consumers choose bulbs that provide the desired amount of light for a given application, while also consuming less energy.
So you are telling me that I can no longer use Watts to measure brightness?
Correct. To measure brightness you have to get with it and use lumens.
OK, got it. But what if I can't wrap my head around Lumens?
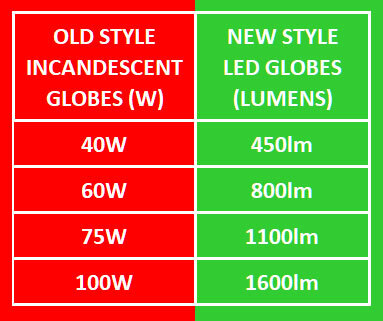
We are here to help - because the sad truth is that everyone over 25 still thinks of brightness in the old Wattage scale of traditional incandescent globes. So we have provided the following fantastic little table that converts Watts (used by the old style traditional incandescent globes) to Lumens (used by the new style LED globes). Please note the comparison is approximate only.
How do we measure lumens?
Lumens are measured using a device called a photometer, which is specifically designed to measure the amount of visible light emitted by a light source. A photometer consists of a sensor that is calibrated to respond to the wavelengths of light that are visible to the human eye, and a meter that displays the measured light intensity in units of lumens.
To measure lumens, the photometer is placed at a specific distance from the light source and pointed directly at it. The sensor then measures the amount of light that is received, and this measurement is used to calculate the total luminous flux, or total amount of visible light emitted by the source. This calculation takes into account the angle at which the light is emitted and the area over which it is distributed.
It's worth noting that the method of measuring lumens can vary depending on the type of light source being measured. For example, for a point source of light, such as a light bulb, the photometer should be placed at a specific distance from the bulb to obtain an accurate measurement. For a large area light source, such as a floodlight, the photometer may need to be moved around to several positions to obtain an accurate measurement across the entire area.
What is the lumen output of a typical LED light bulb?
The lumen output of a typical LED light bulb can vary depending on the specific bulb and its wattage rating. However, in general, LED bulbs are designed to be more energy-efficient than traditional incandescent bulbs while emitting the same amount of light.
For example, a typical 9-watt LED bulb can emit around 800 lumens of light, which is equivalent to the brightness of a 60-watt incandescent bulb. Higher wattage LED bulbs can emit even more lumens. For instance, a 15-watt LED bulb can emit around 1500 lumens, which is equivalent to the brightness of a 100-watt incandescent bulb.
It's worth noting that the lumen output of LED bulbs has been steadily increasing as the technology has advanced, and it's now possible to find LED bulbs with even higher lumen outputs. Additionally, LED bulbs typically have a longer lifespan than traditional incandescent bulbs, making them a more cost-effective and environmentally-friendly choice in the long term.
How does the lumen output of a light bulb affect its energy efficiency?
The lumen output of a light bulb is a measure of the amount of visible light it produces. Generally speaking, a higher lumen output means that the light bulb produces more light, but this does not necessarily mean that it is more energy-efficient.
The energy efficiency of a light bulb is determined by its luminous efficacy, which is the amount of visible light it produces per unit of power input. The higher the luminous efficacy, the more efficient the light bulb is at converting electricity into light.
Therefore, a light bulb with a higher lumen output can still be more energy-efficient if it has a higher luminous efficacy. For example, a LED light bulb with a lower lumen output but a higher luminous efficacy can use less energy to produce the same amount of visible light as a traditional incandescent bulb with a higher lumen output but a lower luminous efficacy.
What is the recommended lumen output for different lighting applications?
The recommended lumen output for different lighting applications can vary depending on the specific needs and preferences of the user. However, here are some general guidelines for common lighting applications:
- Living spaces (e.g., living rooms, bedrooms): 1,500 to 3,000 lumens
- Kitchens and bathrooms: 4,000 to 6,000 lumens
- Workspaces (e.g., home offices, workshops): 3,000 to 6,000 lumens
- Outdoor areas (e.g., porches, pathways): 1,000 to 2,000 lumens
- Retail and commercial spaces: 50 to 100 lumens per square foot, depending on the type of business and desired atmosphere.
It's important to note that the recommended lumen output can also depend on factors such as the size and layout of the space, the type of lighting fixtures used, and personal preferences for brightness and ambiance. When selecting light bulbs or lighting fixtures, it can be helpful to consult with a lighting professional or refer to manufacturer recommendations for the best results.
Do lumens affect the perceived color of light?
Lumens do not directly affect the perceived color of light. Lumen is a unit of measurement for the amount of visible light emitted by a light source, while color temperature is a measure of the color appearance of the light.
Color temperature is measured in Kelvin (K) and describes the appearance of the light source as warm, neutral, or cool. Warm light has a lower color temperature, usually around 2700-3000K, and appears more yellow or orange in color. Cool light has a higher color temperature, usually around 5000-6500K, and appears more blue or white in color. Neutral light has a color temperature of around 4000K and appears more balanced.
So while lumens do not directly affect the color of light, they can impact the perceived brightness and intensity of the light, which can in turn affect how the color of the light appears to the human eye. For example, a light bulb with a high lumen output may appear brighter and more intense, which can make the color of the light appear cooler or more bluish, while a light bulb with a lower lumen output may appear softer and warmer in color.
It's also important to note that the perceived color of light can be affected by the quality of the light source, such as the color rendering index (CRI) and spectral power distribution (SPD). A light source with a high CRI and a balanced SPD can make colors appear more accurate and natural, while a light source with a low CRI or unbalanced SPD can make colors appear distorted or unnatural.
What is the difference between lumens and lux?
Lumens and lux are both measurements of light, but they measure different aspects of light.
Lumens measure the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. It is a measure of the quantity of light emitted and is independent of distance. For example, a light bulb with a higher lumen output will emit more light than a light bulb with a lower lumen output.
Lux, on the other hand, measures the intensity of light at a specific distance from the light source. It is a measure of the amount of light that falls on a given surface area and is dependent on the distance between the light source and the surface. For example, a light source with a higher lumen output will produce a higher lux reading at a given distance than a light source with a lower lumen output.
In other words, lumens measure the total amount of light produced by a light source, while lux measures the amount of light that reaches a surface. Lux is a more useful measurement for determining the level of illumination on a surface, while lumens are more useful for determining the overall brightness of a light source.
What is the history of lumens in lighting?
The history of lumens in lighting can be traced back to the early 20th century, when scientists and engineers began to develop new technologies for measuring and quantifying light. In 1909, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) was established to develop standardized methods for measuring and evaluating light.
One of the key challenges that the CIE faced was developing a standard unit of measurement for light output. At the time, there were several competing units, including candlepower, which measured the brightness of a light source in terms of the amount of light it emitted in a particular direction, and the lumen-hour, which measured the total amount of light emitted by a source over a given period of time.
In 1924, the CIE established the lumen as the standard unit of measurement for light output. The lumen is defined as the amount of light emitted by a source in all directions, with a total output of one candela (a measure of luminous intensity) over a solid angle of one steradian.
Since the establishment of the lumen as the standard unit of measurement for light output, scientists and engineers have continued to develop new technologies for measuring and quantifying light, including the development of more precise instruments for measuring luminous intensity, spectral power distribution, and other properties of light. These advances have helped to drive the development of new lighting technologies, from incandescent bulbs and fluorescent tubes to LEDs and OLEDs, which are more energy-efficient, longer-lasting, and produce higher-quality light than their predecessors.
What is the role of lumens in LED lighting?
The role of lumens in LED lighting is to provide a standardized measure of the amount of light emitted by an LED light source. Lumens are used to quantify the brightness of an LED bulb or fixture, and are a more accurate measure of the amount of visible light that is produced than wattage. When it comes to LED lighting, the lumens-per-watt (LPW) ratio is an important metric for measuring the energy efficiency of LED bulbs and fixtures. The LPW ratio indicates how many lumens of light output are produced for every watt of electricity consumed. Generally, the higher the LPW ratio, the more energy-efficient the LED bulb or fixture. In addition to measuring the brightness and energy efficiency of LED lighting, lumens also play a role in determining the quality of light that is produced. The color temperature and color rendering index (CRI) are two important factors that influence the quality of light produced by LED bulbs and fixtures, and both of these metrics are measured in lumens.
How do lumens affect the safety of outdoor spaces?
Lumens can have a significant impact on the safety of outdoor spaces. In outdoor areas, lighting is often used to improve visibility and reduce the risk of accidents or criminal activity.
By providing adequate illumination, outdoor lighting can help pedestrians and drivers see obstacles, tripping hazards, and other potential safety hazards. High-lumen lighting can also help deter criminal activity, as well-lit areas are less likely to be targeted by criminals.
On the other hand, insufficient lighting can increase the risk of accidents and crime, as poorly-lit areas can make it difficult for people to see potential hazards or identify potential threats. In outdoor spaces, the number of lumens needed for adequate lighting will depend on several factors, including the size and layout of the space, the intended use of the area, and the level of ambient light in the area.
For example, a dimly lit parking lot with poor visibility could pose a safety risk to pedestrians and drivers, while a well-lit pathway with high-lumen lighting can help improve visibility and reduce the risk of tripping or falling.
What is the Australian standard in lumens for various lighting situations?
The Australian standard for lumens for various lighting situations depends on the type of space and the activities that will take place in that space. Here are some general guidelines:
- Living rooms, bedrooms, and hallways typically require 300-400 lumens per square meter.
- Kitchens, bathrooms, and workspaces usually need brighter lighting, with 400-600 lumens per square meter.
- Outdoor areas like gardens and walkways may require 50-300 lumens per square meter, depending on the desired level of brightness.
It's important to note that these are general guidelines and that specific lighting requirements may vary depending on the individual needs of a space or the preferences of the people using it. Additionally, the type of lighting fixture and the color temperature of the bulbs can also affect the perceived brightness of a space.
How do lumens affect the mood of people in a space?
Lumens can have a significant impact on the mood of people in a space. Brighter lighting can create a more energetic and stimulating atmosphere, while dimmer lighting can create a more relaxed and calming environment.
Here are some ways that different levels of lumens can affect mood:
- High lumens: Bright lighting with high lumens can make people feel more alert, energized, and focused. This type of lighting is often used in workspaces, classrooms, and other areas where people need to be alert and attentive.
- Medium lumens: Lighting with medium lumens can create a comfortable and inviting atmosphere. This type of lighting is often used in living rooms, dining rooms, and other areas where people gather and socialize.
- Low lumens: Dimmer lighting with lower lumens can create a more relaxed and calming environment. This type of lighting is often used in bedrooms, bathrooms, and other areas where people want to unwind and relax.
It's important to note that the color temperature of the lighting can also play a role in affecting mood. Cooler, bluer lighting can create a more alert and focused atmosphere, while warmer, yellower lighting can create a more cozy and inviting atmosphere.
What is the relationship between lumens and the quality of light?
The relationship between lumens and the quality of light is an important one when it comes to understanding how different lighting options can impact the overall appearance and feel of a space.
Lumens are a measure of the total amount of light emitted by a source, and are often used as a measure of brightness. However, the quality of light is determined by a number of factors, including color temperature, color rendering index (CRI), and spectral distribution.
Color temperature refers to the perceived warmth or coolness of a light source, and is measured in Kelvin (K). Higher color temperature values (such as 5000K or higher) typically create a cooler, bluer light, while lower values (such as 2700K) create a warmer, yellower light.
CRI is a measure of how accurately a light source renders colors compared to natural sunlight, which has a CRI of 100. Higher CRI values (such as 90 or higher) indicate that colors appear more vibrant and true to life under the light source.
Spectral distribution refers to how light is distributed across the visible spectrum. A more even distribution of light across the spectrum typically results in a higher quality of light, with better color rendering and less harshness or glare.
In general, lighting options that provide higher lumens can create brighter spaces, but they may not necessarily provide the best quality of light. To achieve optimal lighting quality, it's important to consider factors such as color temperature, CRI, and spectral distribution in addition to lumens when selecting lighting options for a space.
What is the importance of lumens in security lighting?
Lumens are a measure of the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source. In the context of security lighting, lumens are important because they directly impact the effectiveness of the lighting in providing a safe and secure environment. High-lumen security lights are brighter and provide better visibility, making it easier to identify potential threats or suspicious activity in the area being illuminated. They also help to deter criminal activity by making it more difficult for intruders to approach a property undetected. However, it's important to note that simply increasing the lumens of a security light does not necessarily make it more effective. Other factors, such as the placement, direction, and color temperature of the light, also play a role in determining how well it performs in a security setting.
What is the relationship between lumens and the angle of light emitted by a source?
The relationship between lumens and the angle of light emitted by a source is indirectly proportional.
When a light source emits light, the light is dispersed in all directions, forming a cone-shaped beam of light. The angle of the cone-shaped beam is known as the beam angle.
A light source with a narrower beam angle will concentrate the light in a smaller area, making the light appear brighter and more intense. However, this also means that the light will cover a smaller area. Conversely, a light source with a wider beam angle will spread the light out over a larger area, making the light appear less intense but covering a larger area.
The total number of lumens emitted by a light source remains constant, regardless of the beam angle. However, the perceived brightness and intensity of the light will vary depending on the beam angle. A light source with a narrow beam angle may appear brighter than a light source with a wider beam angle, even if they have the same number of lumens.
What is the relationship between lumens and the efficiency of a lighting system?
The relationship between lumens and the efficiency of a lighting system is a measure of how effectively a lighting system converts electrical power into visible light.
The efficiency of a lighting system is measured in lumens per watt (lm/W), which is a measure of the amount of visible light produced per unit of electrical power consumed. A lighting system that produces more lumens per watt is considered to be more efficient because it can produce the same amount of light using less electricity.
For example, a lighting system that produces 1000 lumens while consuming 100 watts of power has an efficiency of 10 lm/W (1000 lumens / 100 watts). If a different lighting system produces the same 1000 lumens while consuming only 50 watts of power, its efficiency would be 20 lm/W (1000 lumens / 50 watts).
Therefore, when comparing lighting systems, it's important to consider not only the total number of lumens produced but also the efficiency of the system. A more efficient lighting system will not only save electricity but also reduce operating costs over the lifetime of the system.
What is the relationship between lumens and colour temperature?
The relationship between lumens and color temperature is that both of these lighting characteristics are important in determining the overall appearance and quality of light emitted by a light source.
Lumens are a measure of the total amount of visible light emitted by a light source, while color temperature is a measure of the color appearance of the light emitted by the source. Color temperature is measured in units of Kelvin (K) and refers to the color appearance of the light source, ranging from warm yellowish-white to cool bluish-white.
In general, a light source with a higher number of lumens will be brighter and emit more light than a light source with a lower number of lumens. However, the color temperature of the light can also affect how bright or intense it appears. For example, a light source with a cool, bluish-white color temperature may appear brighter and more intense than a light source with a warm, yellowish-white color temperature, even if they have the same number of lumens.
What is the relationship between lumens and the efficiency of solar-powered lighting?
The relationship between lumens and the efficiency of solar-powered lighting is a critical factor in designing and selecting solar lighting systems.
The efficiency of a solar lighting system is the measure of how effectively it converts the energy from the sun into usable light. Lumens are used to measure the amount of visible light produced by a light source, and the number of lumens produced by a solar-powered lighting system depends on the efficiency of the solar panel and the light fixture.
Solar panels used in solar lighting systems convert sunlight into electrical energy, which is then used to power the lighting system. The efficiency of a solar panel is measured in terms of the percentage of sunlight it converts into electrical energy. The higher the efficiency of the solar panel, the more electrical energy it will produce for a given amount of sunlight.
The efficiency of the light fixture used in a solar lighting system also plays a critical role in determining the number of lumens produced by the system. The light fixture's efficiency refers to the percentage of electrical energy consumed by the fixture that is converted into visible light. Higher efficiency light fixtures will produce more lumens per watt of electrical energy consumed.
Therefore, to maximize the efficiency of a solar lighting system, it's important to use high-efficiency solar panels and light fixtures to ensure that the system can produce the desired amount of visible light while using the minimum amount of energy from the sun.